O-RADS Classification
Risk stratification system for adnexal masses based on ultrasound findings. Identify the O-RADS US category and suggested management according to imaging features and menopausal status.

About O-RADS US
O-RADS US (Ovarian-Adnexal Reporting and Data System Ultrasound) is a standardized risk stratification system for adnexal masses based on ultrasound features.
Version used on the site: O-RADS US v2022: An Update from the American College of Radiology's Ovarian-Adnexal Reporting and Data System US Committee.
O-RADS US 0: Incomplete evaluation
O-RADS US 1: Normal ovary
O-RADS US 2: Almost certainly benign (<1%)
O-RADS US 3: Low risk (<10%)
O-RADS US 4: Intermediate risk (10–<50%)
O-RADS US 5: High risk (≥50%)
O-RADS US Categories
Credit: American College of Radiology (ACR) — O-RADS® (Ovarian-Adnexal Reporting and Data System). Color palette based on ACR material.
O-RADS US 0 — Incomplete Evaluation
Risk: Not assessableThe lesion features relevant to risk stratification cannot be accurately assessed due to technical factors.
Ultrasound findings
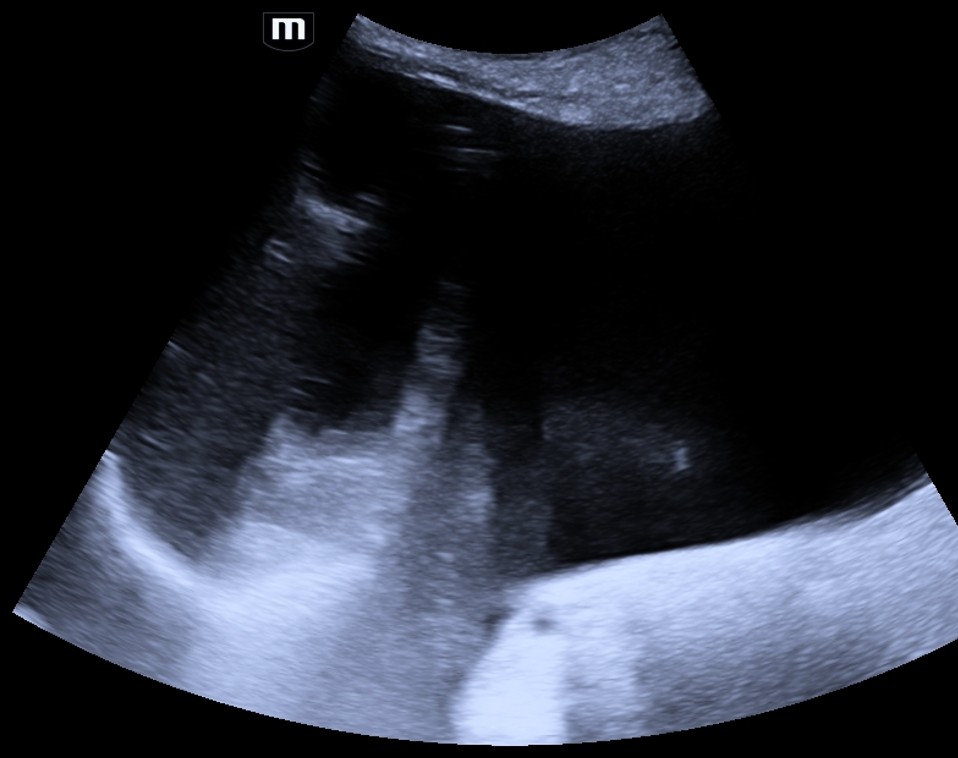
Suggested management
Repeat ultrasound (US) or MRI
O-RADS US 1 — Normal Ovary
Risk: NormalNo ovarian lesion. Normal ovary.
Menopausal status
Ultrasound findings (Pre-menopause)

Suggested management (Pre-menopause)
No management needed
O-RADS US 2 — Almost Certainly Benign
Risk: <1%Simple smooth unilocular cysts and classic benign lesions (hemorrhagic, dermoid, endometrioma, paraovarian, peritoneal inclusion cyst, hydrosalpinx).
Menopausal status
Simple cyst

Smooth non-simple unilocular/bilocular cyst
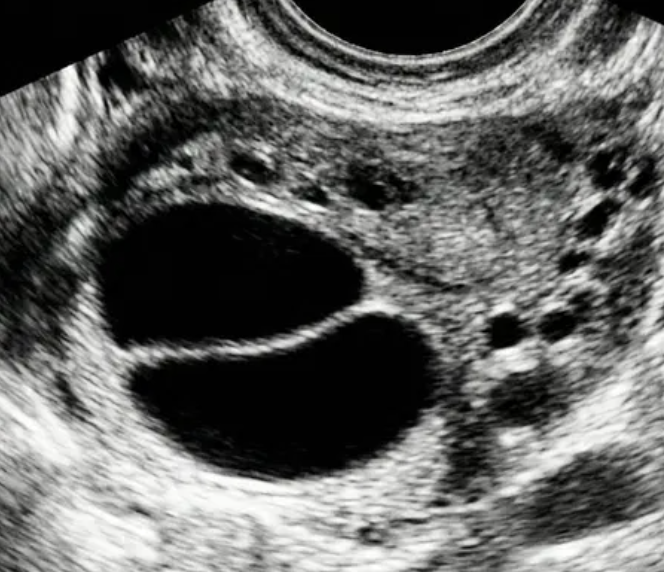

Classic benign lesion



O-RADS US 3 — Low Risk of Malignancy
Risk: <10%Typically benign ovarian lesions ≥10 cm and other low-risk findings (large smooth cysts, irregular inner wall <3 mm, multilocular <10 cm with smooth wall, solid lesions with smooth surface).
Typically benign ovarian lesions ≥ 10 cm

Other lesions
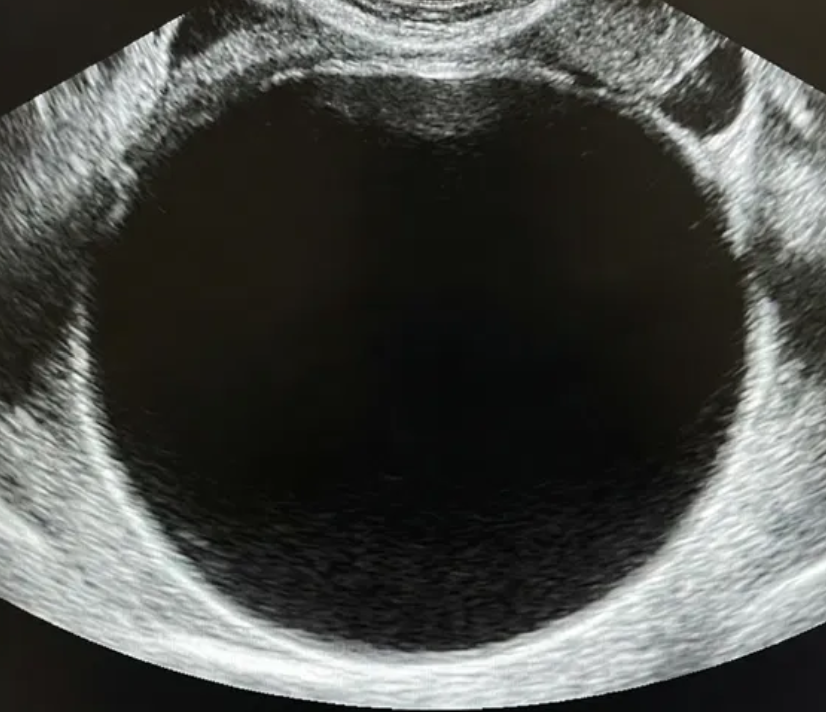
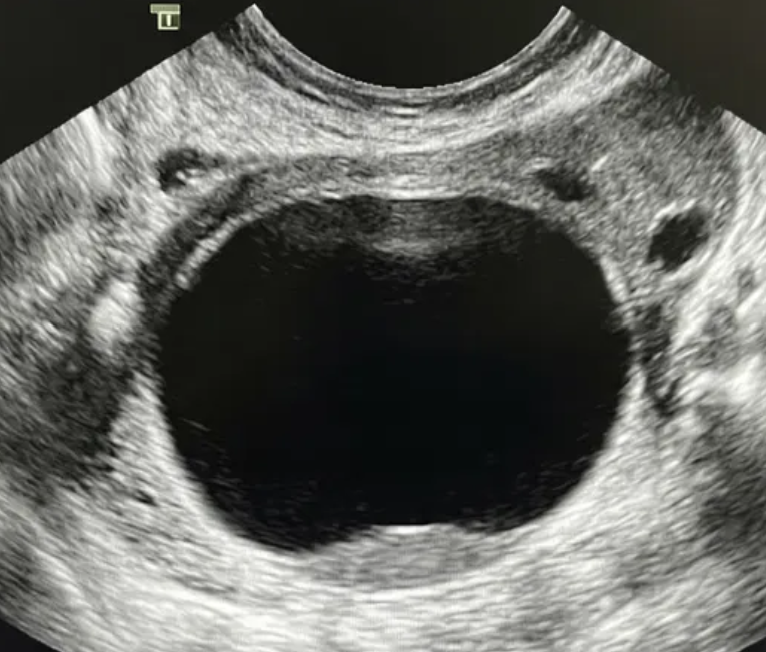

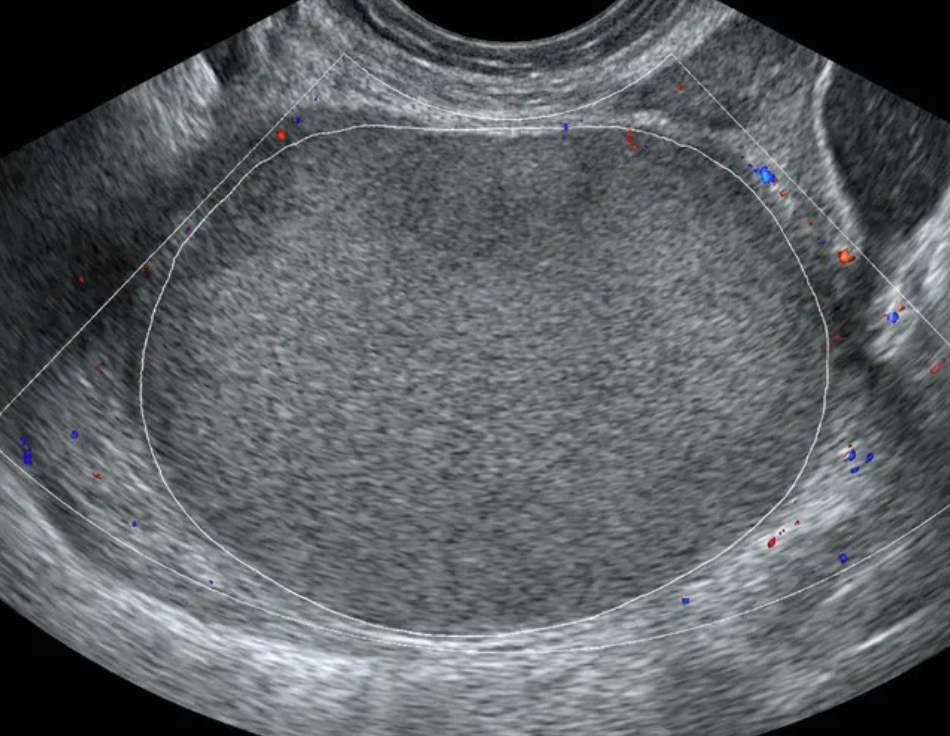
Suggested management
If not surgically removed, consider follow-up US at 6 months. In some scenarios, shorter imaging follow-up may be considered (e.g., clinical factors). During follow-up: • If smaller (≥10–15% decrease in average linear dimension), no further surveillance. • If stable, follow-up US at 24 months from the initial exam. • If enlarging (≥10–15% increase in average linear dimension), consider follow-up US at 12 and 24 months from the initial exam, then manage per gynecology. • For changing morphology, reassess using lexicon descriptors. • Clinical management with gynecology as needed. • For solid lesions, consider specialist US (if available) or MRI (with O-RADS MRI score).
O-RADS US 4 — Intermediate Risk
Risk: 10-<50%Multilocular cyst without solid component ≥10 cm or with CS = 4, unilocular/multilocular cyst with a solid component, solid lesion with smooth surface and CS = 2–3.
Bilocular cyst without solid component
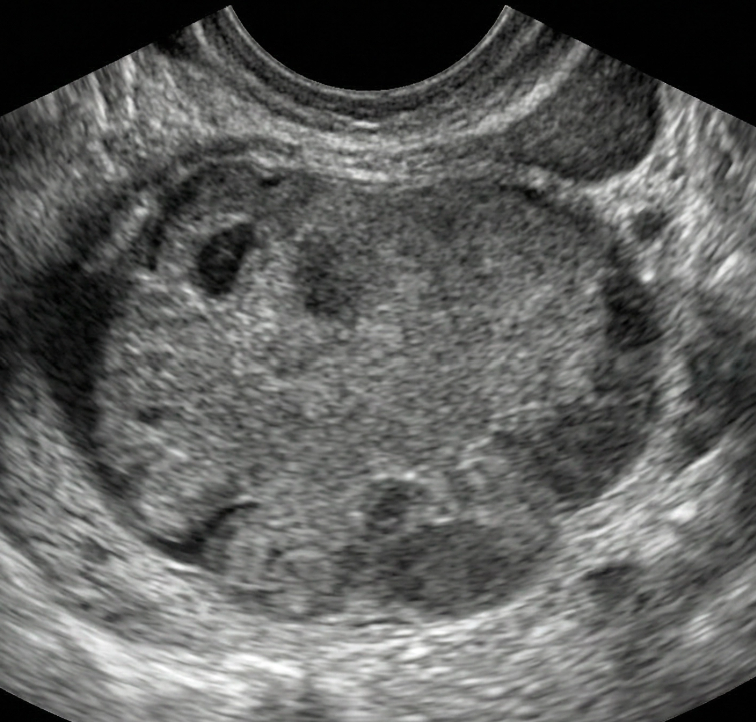
Multilocular cyst without solid component
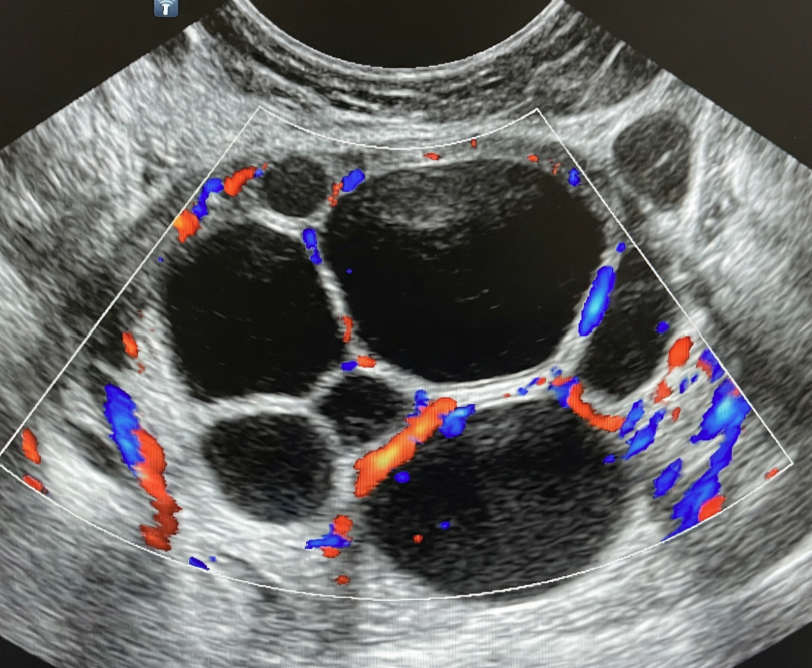
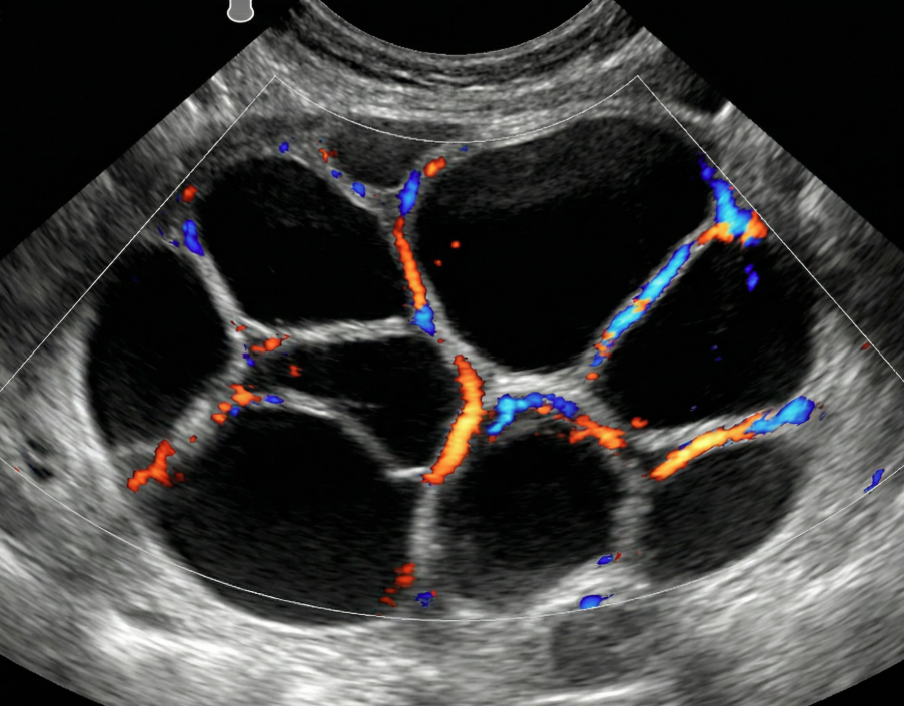
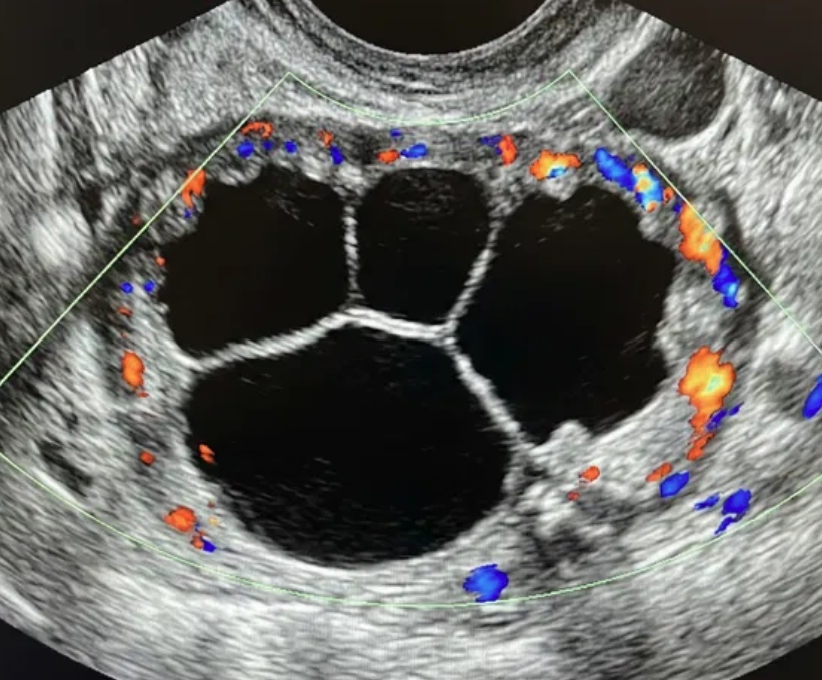
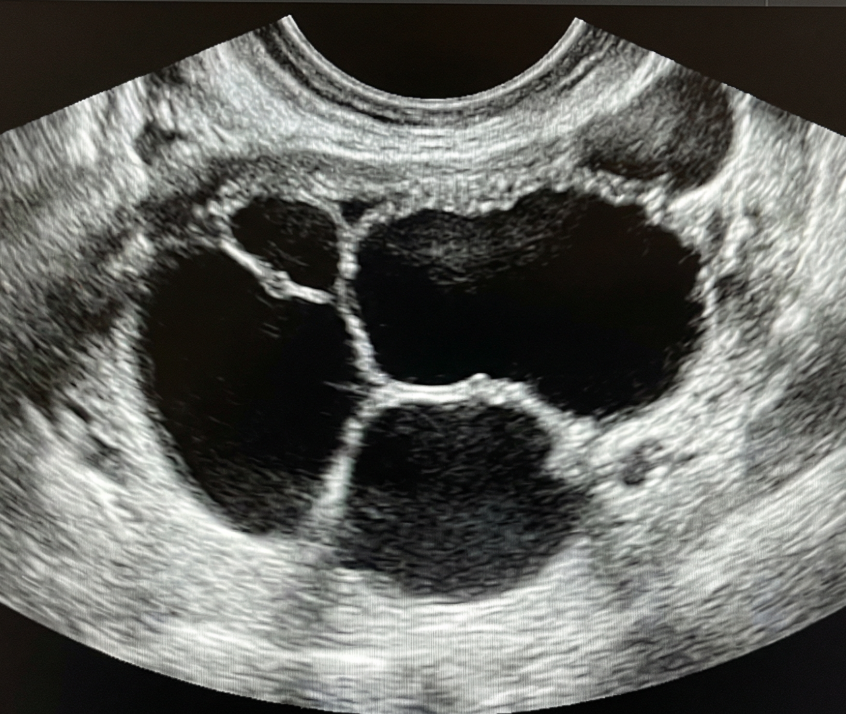
Unilocular cyst with solid component

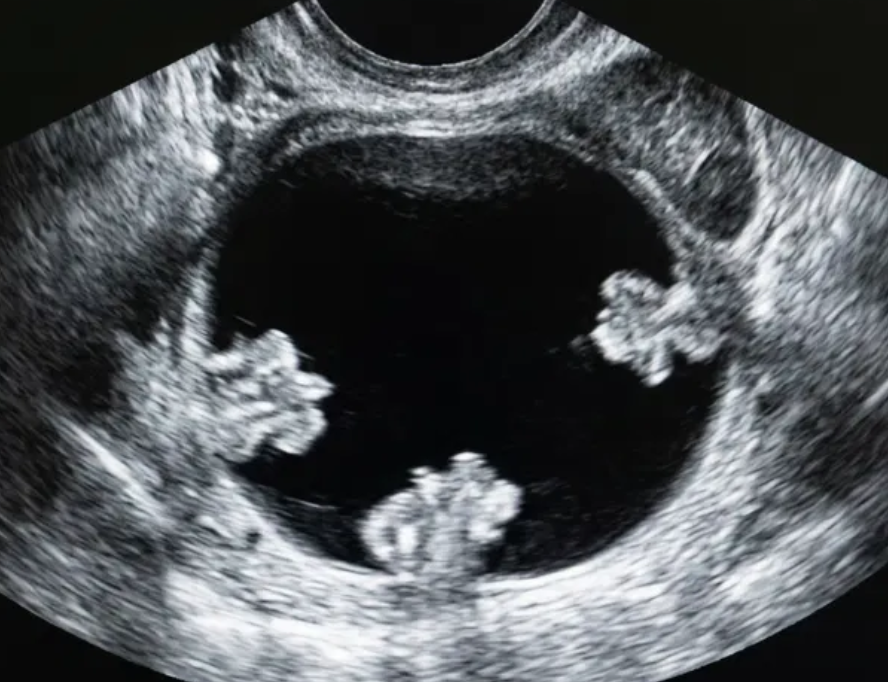
Multilocular cyst with solid component
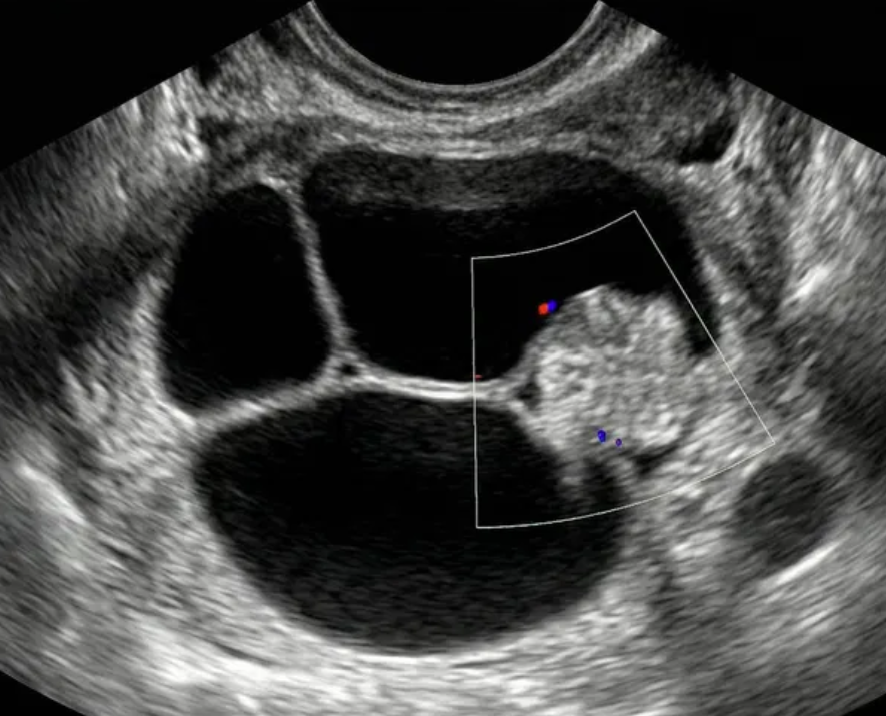
Solid lesion
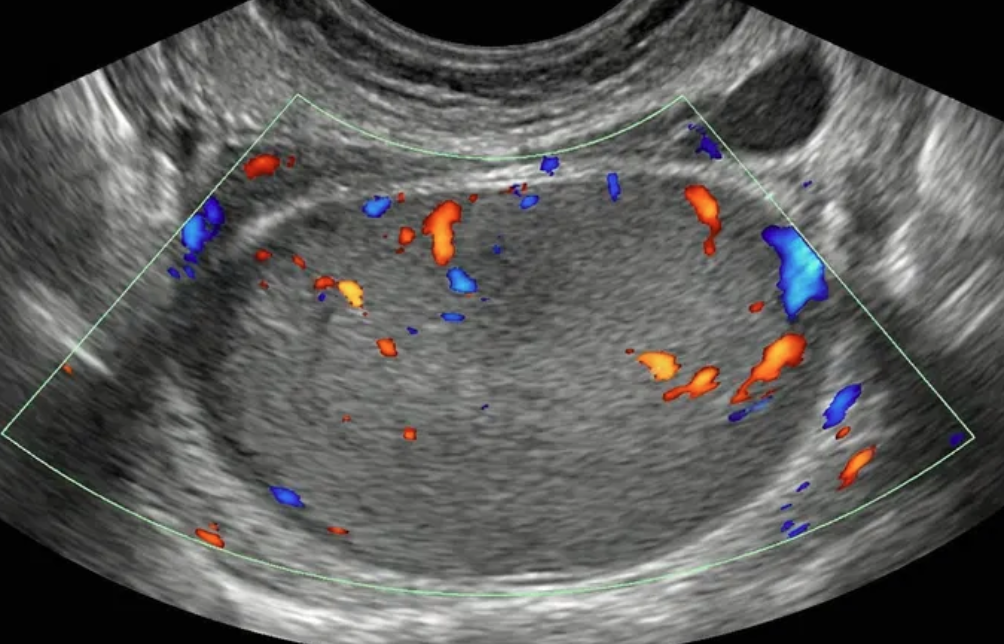
Suggested management
Imaging options include specialist US (if available) and MRI (with O-RADS MRI score), per gynecologic oncologist protocol. Management by gynecology with consultation with gynecologic oncology or directly by gynecologic oncology.
O-RADS US 5 — High Risk
Risk: ≥50%Unilocular cyst with ≥4 papillary projections, multilocular cyst with solid component and CS = 3–4, solid lesion with CS = 4 or irregular surface, ascites and/or peritoneal nodules.
Unilocular cyst (papillae)

Multilocular cyst with solid component
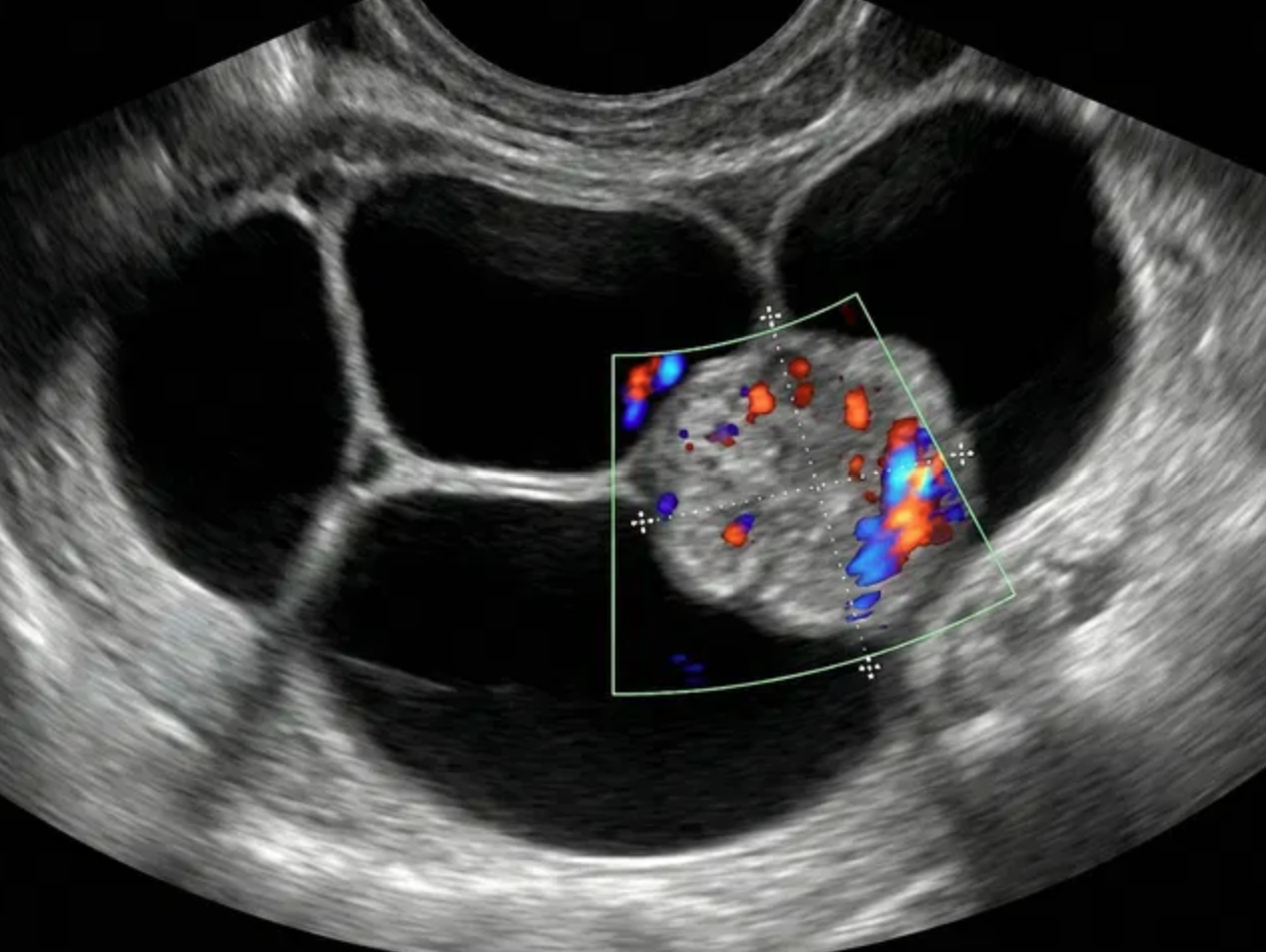
Solid lesion
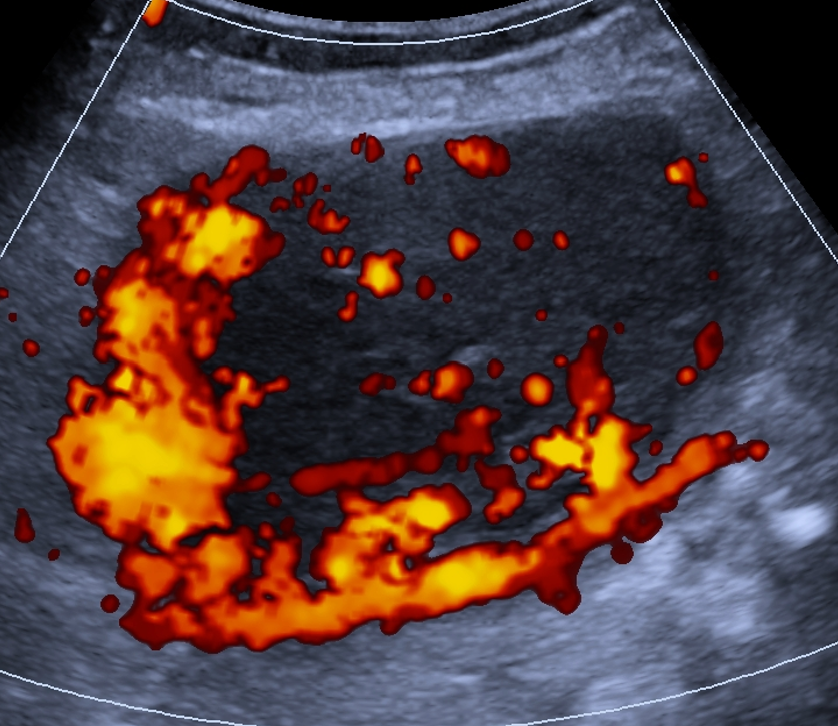
Additional findings

Suggested management
Management by gynecologic oncology
Glossary
Smooth and irregular
refer to inner walls/septation(s) for cystic lesions, and outer contour for solid lesions; irregular inner wall for cysts = <3 mm in height
Shadowing
must be diffuse or broad to qualify; excludes refractive artifact
CS
color score; degree of intralesional vascularity; 1 = none, 2 = minimal flow, 3 = moderate flow, 4 = very strong flow
Solid
excludes blood products and dermoid contents; solid lesion = ≥80% solid; solid component = protrudes ≥3 mm (height) into cyst lumen off wall or septation
PP
papillary projection; subtype of solid component surrounded by fluid on 3 sides
Bilocular / multilocular
Bilocular = 2 locules; multilocular = ≥3 locules; bilocular smooth cysts have a lower risk of malignancy, regardless of size or CS
References
Strachowski LM, Jha P, Phillips CH, Blanchette Porter MM, Froyman W, Glanc P, Guo Y, Patel MD, Reinhold C, Suh-Burgmann EJ, Timmerman D, Andreotti RF. O-RADS US v2022: An Update from the American College of Radiology's Ovarian-Adnexal Reporting and Data System US Committee. Radiology. 2023 Sep;308(3):e230685. doi: 10.1148/radiol.230685. PMID: 37698472.
Andreotti RF, Timmerman D, Strachowski LM, Froyman W, Benacerraf BR, Bennett GL, Bourne T, Brown DL, Coleman BG, Frates MC, Goldstein SR, Hamper UM, Horrow MM, Hernanz-Schulman M, Reinhold C, Rose SL, Whitcomb BP, Wolfman WL, Glanc P. O-RADS US Risk Stratification and Management System: A Consensus Guideline from the ACR Ovarian-Adnexal Reporting and Data System Committee. Radiology. 2020 Jan;294(1):168-185. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2019191150. Epub 2019 Nov 5. PMID: 31687921.